



WGS 84 / NAD 83 - A Standard Datum in Several Names
With the advent of satellite navigation systems, it was possible to construct a world wide datum. These are labeled Geodetic Systems. These were generated by the US Department of Defense beginning in 1966. They constructed World Geodetic System 1966 (WGS 66), which was not very good. It was followed by WGS 72 which was much better and then WGS 84. The Soviet Union also constructed a series of these, called SRS's with the last being SRS 90. It should be noted that these WGS's include information about the gravity field as well as an ellipsoid and a realization of the "datum".
WGS 84 is the current standard in the west. The US civilian survey organization, the National Geodetic Survey (NGS) generated a new datum for North America at the same time. It is essentially identical to WGS 84 - version 1.
The world geodesy community has been generating these geodetic reference systems since the mid 1990's. These are labeled International Terrestrial Reference Systems ( ITRF's ). There have been ITRF 96, ITRF 98 etc. As these became refined, the changes became smaller. They were converging on the real world. In fact, the current versions include a model of the motion of the crustal plates. This is necessary to preserve the accuracy. (Monterey California, for example, is on the Pacific Plate and moving north west at 6 cm per year with respect to the North American Plate only a dozen kilometers inland).
The US civilian agencies have adopted new a new datum in 2000. The US Department of Defense has essentially done the same thing, but has kept the name WGS 84. Rather than change the coordinates of all its know bench marks, it has adjusted the coordinates of the reference sites used to generate the orbits with the Global Positioning System. Thus the positions obtained using the over the air ephemeris and no Differential GPS corrections have changed. GPS counts time in weeks since 1980. The new datums are labeled
WGS 84 (G730) implemented in January 1994 ( GPS Week 730) and,
WGS 84 (G873) implemented in September 1996.
These brought WGS into alignment with ITRF 94 and ITRF 96 at the few cm level.
The civilian agencies in the US have been using differential GPS survey techniques to generate a realization of a new network at better than one part per million (1 ppm or 1 cm over 10 km). They have achieved an order of magnitude better (0.1 ppm) in most areas. They have a goal of a High Accuracy Reference Network (HARN) survey marker within 200 km of anyplace in the US.
This contains most of the markers used to define NAD 83, in effect allowing a redefinition of that datum. A new NAD 2000 is being released. Here is the real primary control network of the US - the HARN network. This is the realization – how the datum is really used.
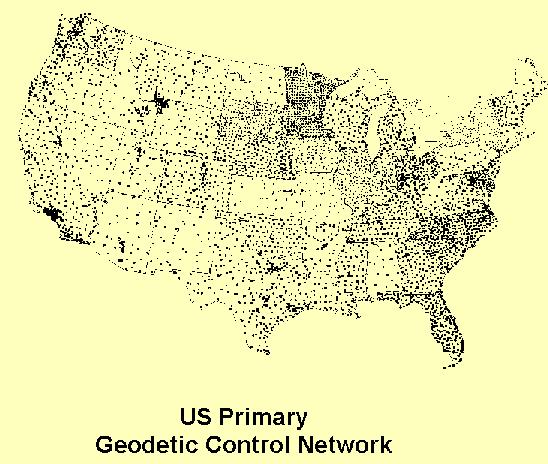
The official, high accuracy, coordinates of these points are on file with the US National Geodetic Survey (NGS). They can be retrieved from the NGS web site.
Note:
The vertical networks have typically been separate from the horizontal network. The NAD 83 was followed by the North American Vertical Datum of 1988 (NAVD 88). Vertical networks are very closely tied to the gravitational model used in these systems.
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|